Setting Up
Generating an API Key
To use the UmamiAI API, you need to create an account and generate an API key. Follow these steps:
- Create an Account: Visit the UmamiAI API website and create an account.
- Generate an API Key: After logging in, navigate to your account dashboard and generate your API key. Ensure that key is enabled on UI.
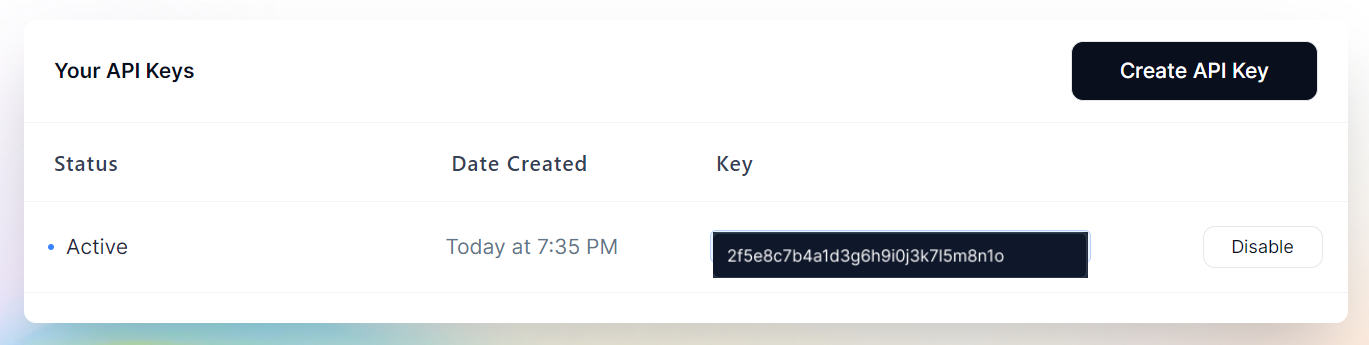
Your API key
Configure Base URL
Depending on your environment and application, you will set the base URL differently. Below is a universal string that you can use to access our API. Copy it or return here later when you are ready with your environment or app.
https://api.umamiai.xyz/v1
https://api.umami-ai.xyz/v1
The UmamiAI API supports both versioned URLs, providing flexibility in your API requests. You can use either of the following formats:
https://api.umamiai.xyz/v1https://api.umamiai.xyz/v2Please refer api docshttps://api.umami-ai.xyz/v1https://api.umami-ai.xyz/v2Please refer api docs
Making Your First API Call
Based on your environment, you will call our API differently. Below are two common ways to call our API using two popular programming languages: Python and NodeJS.
In the examples below, we use the OpenAI SDK. This is possible due to our compatibility with most OpenAI APIs, but this is just one approach. You can use our API without this SDK with raw HTTP queries.
Example in Python
Let's start from very beginning. We assume you already installed Python (with venv), if not, here a guide for the beginners.
Create a new folder for test project, name it as umamiai-welcome and change to it.
mkdir ./umamiai-welcome
cd ./umamiai-welcome
(Optional) If you use IDE then we recommend to open created folder as workspace. On example, in VSCode you can do it with:
code .
Run a terminal inside created folder and create virtual envorinment with a command
python3 -m venv ./.venv
Activate created virtual environment
# Linux / Mac
source ./.venv/bin/activate
# Windows
./.venv/bin/Activate.bat
Install requirement dependencies. In our case we need only OpenAI SDK
pip install openai
Create new file and name it as travel.py
touch travel.py
Paste following content inside this travel.py and replace my_key with your API key you got on first step
from openai import OpenAI
base_url = "https://api.umamiai.xyz/v1"
api_key = "my_key"
system_prompt = "You are a travel agent. Be descriptive and helpful."
user_prompt = "Tell me about San Francisco"
api = OpenAI(api_key=api_key, base_url=base_url)
def main():
completion = api.chat.completions.create(
model="mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt},
],
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=256,
)
response = completion.choices[0].message.content
print("User:", user_prompt)
print("AI:", response)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Run the application
python3 ./travel.py
If you done all correct, you will see following output:
User: Tell me about San Francisco
AI: San Francisco, located in northern California, USA, is a vibrant and culturally rich city known for its iconic landmarks, beautiful vistas, and diverse neighborhoods. It's a popular tourist destination famous for its iconic Golden Gate Bridge, which spans the entrance to the San Francisco Bay, and the iconic Alcatraz Island, home to the infamous federal prison.
The city's famous hills offer stunning views of the bay and the cityscape. Lombard Street, the "crookedest street in the world," is a must-see attraction, with its zigzagging pavement and colorful gardens. Ferry Building Marketplace is a great place to explore local food and artisanal products, and the Pier 39 area is home to sea lions, shops, and restaurants.
San Francisco's diverse neighborhoods each have their unique character. The historic Chinatown is the oldest in North America, while the colorful streets of the Mission District are known for their murals and Latin American culture. The Castro District is famous for its LGBTQ+ community and vibrant nightlife.
Example in NodeJS
As in the example from Python, we start from the very beginning too. We assume you already have Node.js installed. If not, here is a guide for beginners.
We need to create a new folder for the example project:
mkdir ./umamiai-welcome
cd ./umamiai-welcome
(Optional) If you use IDE then we recommend to open created folder as workspace. On example, in VSCode you can do it with:
code .
Now create a project file:
npm init -y
Install the required dependencies:
npm i openai
Create a file with the source code:
touch ./index.js
And paste the following content:
const { OpenAI } = require("openai");
const baseURL = "https://api.umamiai.xyz/v1";
const apiKey = "my_key";
const systemPrompt = "You are a travel agent. Be descriptive and helpful";
const userPrompt = "Tell me about San Francisco";
const api = new OpenAI({
apiKey,
baseURL,
});
const main = async () => {
const completion = await api.chat.completions.create({
model: "mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: systemPrompt,
},
{
role: "user",
content: userPrompt,
},
],
temperature: 0.7,
max_tokens: 256,
});
const response = completion.choices[0].message.content;
console.log("User:", userPrompt);
console.log("AI:", response);
};
main();
You will see a response that looks like this:
User: Tell me about San Francisco
AI: San Francisco, located in the northern part of California, USA, is a vibrant and culturally rich city known for its iconic landmarks, beautiful scenery, and diverse neighborhoods.
The city is famous for its iconic Golden Gate Bridge, an engineering marvel and one of the most recognized structures in the world. Spanning the Golden Gate Strait, this red-orange suspension bridge connects San Francisco to Marin County and offers breathtaking views of the San Francisco Bay and the Pacific Ocean.
Code Explanation
Both examples are written in different programming languages, but despite that, they look very similar. Let's break down the code step by step and see what's going on.
In the examples above, we are using the OpenAI SDK. The OpenAI SDK is a nice module that allows us to use the UmamiAI API without dealing with repetitive boilerplate code for handling HTTP requests. Before we can use the OpenAI SDK, it needs to be imported. The import happens in the following places:
JavaScript
const { OpenAI } = require("openai");
Python
from openai import OpenAI
Simple as it is. The next step is to initialize variables that our code will use. The two main ones are: the base URL and the API key. We already discussed them at the beginning of the article.
JavaScript
const baseURL = "https://api.umamiai.xyz/v1";
const apiKey = "my_key";
const systemPrompt = "You are a travel agent. Be descriptive and helpful";
const userPrompt = "Tell me about San Francisco";
Python
base_url = "https://api.umamiai.xyz/v1"
api_key = "my_key"
system_prompt = "You are a travel agent. Be descriptive and helpful."
user_prompt = "Tell me about San Francisco"
To communicate with LLM models, users use texts. These texts are usually called "Prompts." Inside our code, we have prompts with two roles: the system and the user. The system prompt is designed to be the main source of instruction for LLM generation, while the user prompt is designed to be user input, the subject of the system prompt. Despite that many models can operate differently, this behavior usually applies to chat LLM models, currently one of the most useful and popular ones.
Inside the code, the prompts are called in variables systemPrompt, userPrompt in JS, and system_prompt, user_prompt in Python.
Before we use the API, we need to create an instance of the OpenAI SDK class. It allows us to use all their methods. The instance is created with our imported package, and here we forward two main parameters: the base URL and the API key.
JavaScript
const api = new OpenAI({
apiKey,
baseURL,
});
Python
api = OpenAI(api_key=api_key, base_url=base_url)
Because of notation, these two parameters are called slightly differently in these different languages (camel case in JS and snake case in Python), but their functionality is the same.
All preparation steps are done. Now we need to write our functionality and create something great. In the examples above, we make the simplest travel agent. Let's break down the steps of how we send a request to the model.
The best practice is to split the code blocks into complete parts with their own logic and not place executable code inside global module code. This rule applies in both languages we discuss. So we create a main function with all our logic. In JS, this function needs to be async, due to Promises and simplicity. In Python, requests run synchronously.
The OpenAI SDK provides us with methods to communicate with chat models. It is placed inside the chat.completions.create function. This function accepts multiple parameters but requires only two: model and messages.
model is a string, the name of the model that you want to use. For the best results, use a model designed for chat, or you can get unpredictable results if the model is not fine-tuned for that purpose. A list of supported models can be found here.
messages is an array of objects with a content field as prompt and a role string that can be one of system, user, tool, assistant. With the role, the model can understand what to do with this prompt: Is this an instruction? Is this a user message? Is this an example of how to answer? Is this the result of code execution? The tool role is used for more complex behavior and will be discussed in another article.
In our example, we also use max_tokens and temperature. How to use these parameters is discussed in the parameters article.
With that knowledge, we can now send our request like the following:
JavaScript
const completion = await api.chat.completions.create({
model: "mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: systemPrompt,
},
{
role: "user",
content: userPrompt,
},
],
temperature: 0.7,
max_tokens: 256,
});
Python
completion = api.chat.completions.create(
model="mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt},
],
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=256,
)
The response from the function chat.completions.create contains a completion. Completion is a fundamental part of LLM models' logic. Every LLM model is some sort of word autocomplete engine, trained by huge amounts of data. The chat models are designed to autocomplete large chunks of messages with prompts and certain roles, but other models can have their own custom logic without even roles.
Inside this completion, we are interested in the text of the generation. We can get it by getting the result from the completion variable:
JavaScript
const response = completion.choices[0].message.content;
Python
response = completion.choices[0].message.content
In certain cases, completion can have multiple results. These results are called choices. Every choice has a message, the product of generation. The string content is placed inside the content variable, which we placed inside our response variable above.
In the next steps, we can finally see the results. In both examples, we print the user prompt and response like it was a conversation:
JavaScript
console.log("User:", userPrompt);
console.log("AI:", response);
Python
print("User:", user_prompt)
print("AI:", response)
Voila! Using UmamiAI API models is the simplest and most productive way to get into the world of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.